People Tagging (SOBOLEO)
Knowing-who is an essential element for efficient knowledge maturing processes, e.g. for finding the right person to talk to. Many approaches like self-descriptions in employee yellow pages, or top-down competence management approaches have largely failed to live up to their promises. Often because information contained in the directories becomes outdated quickly; or is not described in a manner relevant to potential users.
The approach: Collaborative People Tagging
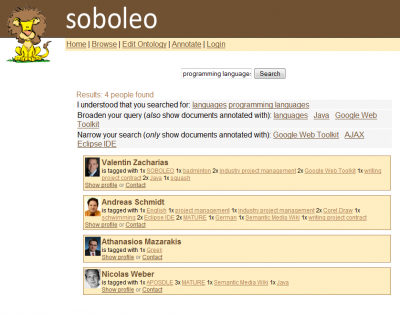
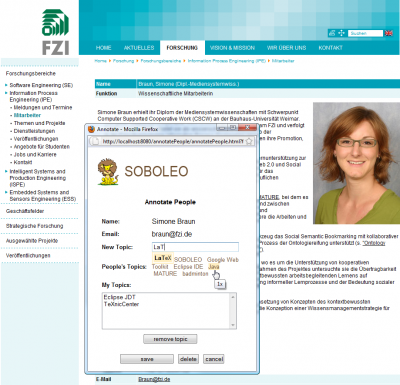
In MATURE, we are using a lightweight approach based on collaborative tagging as a principle to gather the information about persons inside and outside the company (if and where relevant): individuals tag each other according to the topics they associate with this person. We call this ‘people tagging’. In this way, we gain a collective review of existing skills and competencies. Knowledge can be shared and awareness strengthened within the organisational context around who knows what. This tagging information can then be used to search for persons to talk to in a particular situation. Moreover it can also be used for various other purposes. For instance, human resource development needs to have sufficient information about the needs and current capabilities of their workforce.
Foundation: Collaborative construction of a shared understanding
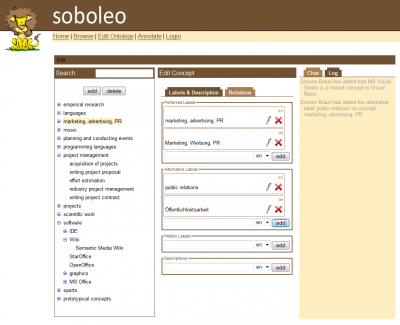
This needs continuous development of a shared vocabulary (ontology). Competencies usually have an integrating function in the enterprise, bringing together strategic and operational levels, and human resources, and performance management aspects.so that these notions have to be shared by the whole organization (in the ideal case): in consequence we cannot do this without a shared vocabulary – a shared vocabulary which the employees evolve in its usage, i.e. during the tagging or search process.
With our tools, the employees can tag each other with concepts from the shared vocabulary. In the case they want to tag with a topic the existing ontology concepts do not cover (e.g. because the topic is too new or specific), the employees can adapt an existing concept or just use a new term, without an agreed meaning. These new terms are automatically added to the shared vocabulary as “prototypical concepts”, reflecting the fact that it’s not clear yet how they relate to the existing concepts. The users can then remove the new terms from the “prototypical concepts” container and integrate them into the vocabulary and add additional information. The vocabulary information is also used as background knowledge to support the search process. That means the users can improve the retrieval by adding and refining vocabulary information. For instance, if the users miss entries in the search results because of missing links between concepts (e.g. entries with ‘Glasgow’ or ‘Edinburgh’ when searching for ‘Scotland’), they can easily add them. In this way, we can achieve a collaborative and incremental in-situ revision and improvement. Realtime collaborative gardening tools are provided to promote the convergence towards a shared vocabulary
MATURE explores the relationship of organizational culture and other specifics, e.g. tag/tagger visibility, degree of control for tags, reconcilability with works council etc., as well as the potential of analyzing the tagging dynamics for informing HR development strategies, e.g. identification of crucial new topics and developments.
Presentations
Flyer
A flyer describing the people tagging demonstrator is available here.